A work energy bar chart represents the amount of energy possessed by an object by means of a vertical bar.
Work energy theorem illustration.
The length of the bar is representative of the amount of energy present with a longer bar representing a greater amount of energy.
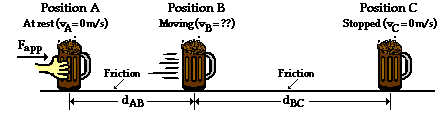
Find the speed of the package in figure 3 at the end of the push using work and energy concepts.
If you don t do work at all then the kinetic energy will not change.
We apply the work energy theorem.
So when velocities are given work done can be calculated directly by using the work energy theorem.
For example you are working right now on your grasp of physics by reading this article.
It basically says when you do work you either add or you remove the kinetic energy from the body.
The work energy theorem explains the reasons behind this physics of no work.
A brick is dropped from a height of.
So negative work removes kinetic energy from the body.
Here the work energy theorem can be used because we have just calculated the net work w net and the initial kinetic energy.
Significance we could have used newton s second law and kinematics in this example but the work energy theorem also supplies an answer to less simple situations.
And this is crudely speaking what we call the work energy theorem.
If there is no displacement there is no work done.
Anyways this much kinetic energy is removed so by definition this is the work done on the tempo.
One tool which can be utilized to express an understanding of the work energy theorem is a bar chart.
The penetration of a bullet fired vertically upward into a block of wood is discussed in one section of asif shakur s recent article bullet block science video puzzle.
Therefore we first need to determine the car s kinetic energy at the moment of braking using.
We know that all the car s kinetic energy is lost to friction.
This definition can be extended to rigid bodies by defining the work of the torque and rotational kinetic energy.
Calculate the work that has been done on the brick between the moment it is released and the moment when it hits the ground.
Determining speed from work and energy.
The principle of work and kinetic energy also known as the work energy theorem states that the work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle.
Therefore the change in the car s kinetic energy is equal to the work done by the frictional force of the car s brakes.
Work is said to be done when an acting force displaces a particle.
But physics itself might not agree on this.